dicot seed diagram
Prothallus of a fern - Haploid. Which criteria are used for the classification of plants.

Assignment 12 Page 4
He did not articulate a formal classification scheme but relied on the common groupings of folk taxonomy combined with growth form.
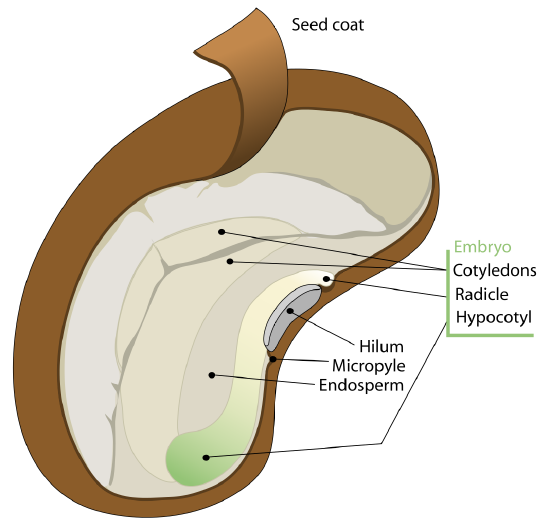
. The Seed The ovules after fertilization develop into the seeds. Citation neededThe stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa.
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant the other being the rootIt supports leaves flowers and fruits transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem stores nutrients and produces new living tissue. Stomata are structures present in the epidermis of leaves. The soybean soy bean or soya bean Glycine max is a species of legume native to East Asia widely grown for its edible bean which has numerous uses.
Observe the plants carefully and describe them in scientific language. Each stoma is composed of two bean-shaped cells known as guard cells which enclose stomatal pore. Fruit is a ripened ovary.
Cells are the basic building block of all living things. Practice diagram-based questions these are very popular. Formation of globular and heart-shaped embryo occurs which finally becomes horseshoe-shaped mature embryo.
Leaf Anatomy Schematic diagram of the anatomy of a leaf. Diagram of the internal structure of a dicot seed and embryo. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphologyFor other related terms see Glossary of phytopathology and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic.
Download scientific diagram Genome-wide identification of NUP1-enriched regions in various tissues. Embryo Development in Dicot Seed. Primary endosperm nucleus in a dicot - Triploid.
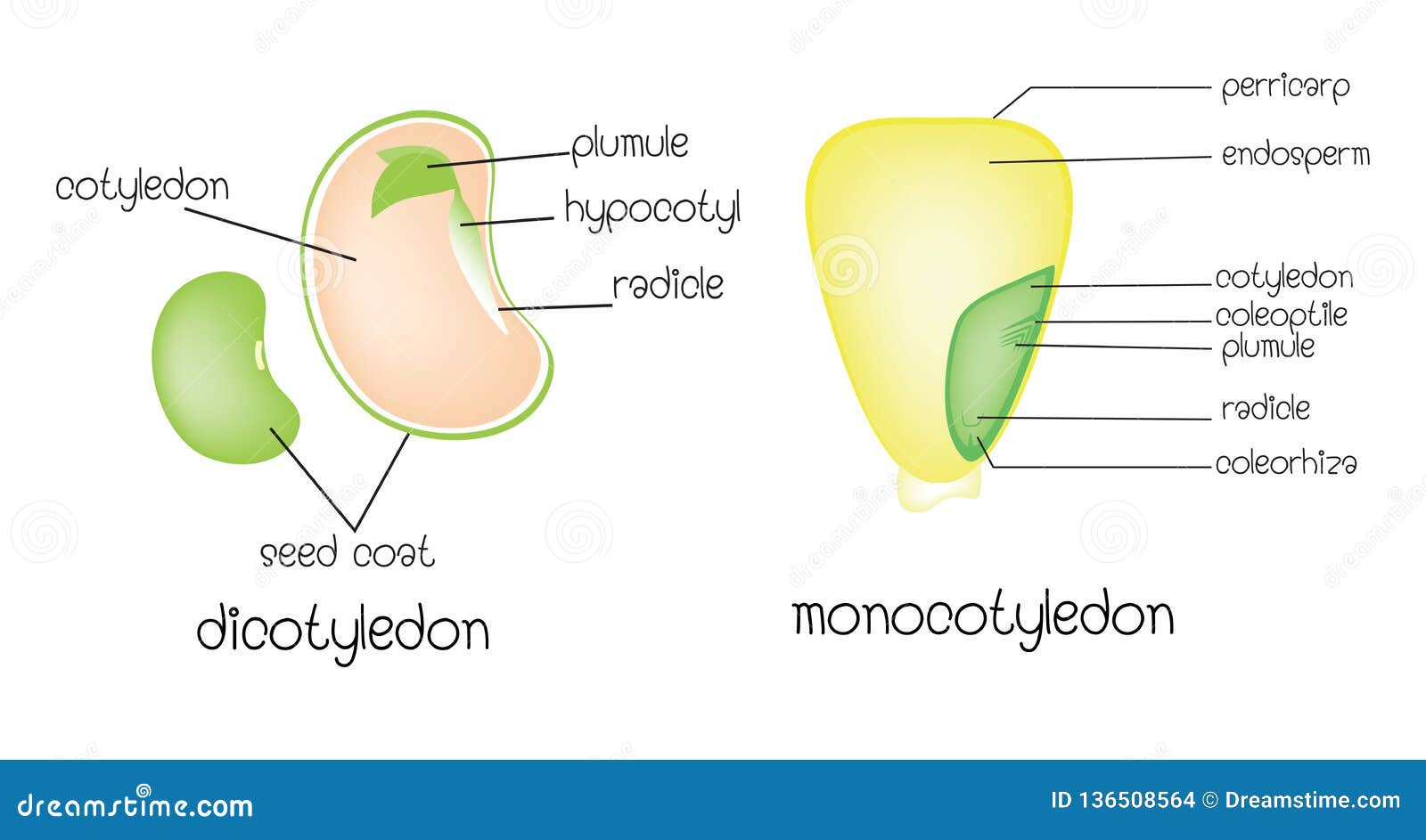
Different embryos between a dicot bean and a monocot grain. Xylem vs Phloem- Definition 18 Major Differences Examples. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk from which tofu and tofu skin are made.
Epidermis mesophyll and veinsor vascular bundles. A Signals of NUP1GFP RE-ChIP-seq 20-kb window size represented as the log 2 value of the. Leaves is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesisLeaves are collectively called foliage as in autumn foliage while the leaves stem flower and fruit collectively form the shoot system.
Leaf cell of a moss - Haploid. Explain the structure of stomata with a labelled diagram. There are many different kinds of seeds.
Different parts of a monocot and dicot seed its. Plant Kingdom Biology Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type. Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that through cellular respiration can later be released to fuel the organisms activitiesSome of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules such as sugars and starches which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water hence the name.
A chloroplast ˈ k l ɔːr ə ˌ p l æ s t-p l ɑː s t is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cellsThe photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight converts it and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. It results in the formation of the seedling. It is considered a crucial step in evolution as it is a precursor to the seed habit.
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits and form the clade Angiospermae ˌ æ n dʒ i ə ˈ s p ɜːr m iː commonly called angiospermsThe term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words angeion container vessel and sperma seed and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruitThey are by far the most diverse group of land. These plants are deciduous and unique among gymnosperms for forming seed cones in female plants instead of a group of leaf-life structure megasporophyll with seeds in male individuals. Inside a seed is a plant embryo which is the baby plant a protective barrier one or two embryonic leaves and a source of food.
In most leaves the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the. A seed is the part of a seed plant which can grow into a new plant. Collect a monocot and dicot plant available in your area.
The ATP and NADPH. Define a seed. Monocot vs Dicot Roots- Definition Structure 18 Differences Examples.
These basic elements are expressed differently in different. Zephyris CC BY-SA 30 Epidermis. We conclude that graft compatibility is a shared ability among seed-bearing plants.
Germination is usually the growth of a plant contained within a seed. If plants do not bear flowers fruits and seeds they are non-seed bearing plants. The peripatetic philosopher Theophrastus 372287 BC as a student of Aristotle in Ancient Greece wrote Historia Plantarum the earliest surviving treatise on plants where he listed the names of over 500 plant species.
It is a reproductive structure which disperses and can survive for some time. Give one example of a dicot seed and one of a monocot seed. Some plants make a lot of seeds some make only a.
Diagram of a generalized dicot seed 1 versus a generalized monocot seed 2. Germination is of epigeal type Fig. In gymnosperms and angiosperms this ultimately led to the development of seeds.
This page provides a glossary of plant morphologyBotanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. 1 an embryo 2 a supply of nutrients for the embryo and 3 a seed coat. The cotyledons are pushed out of the seed.
The main elements can look vastly different between species. The first pair of foliage leaves is produced by the development of plumule. The epidermal layer is one cell thick and covers the entire surface of the leaf.
Diagram via Plants Grow Here. The seed of a vascular plant is a small package produced in a fruit or cone after the union of male and female reproductive cells. It is a ripened ovule and capable of forming a new plant.
In cross-section there are three major regions to see in the inside of a leaf. An embryo is made up of an embryonic axis having plumule and radicle with one or two cotyledons One cotyledon Example Maize Two cotyledon Example -. A seed is made up of seed coat and an embryo.
In dicot plant embryo consists of two cotyledons and an embryonal axis between them. Embryo formation starts after a certain amount of endosperm is formed. The first green leaves of the plant are formed by the cotyledons.
The hypocotyl elongates and this brings the cotyledons out of the soil. A seed coat b. It is also the process of reactivation of metabolic machinery of the seed resulting in the emergence of radicle and plumule.
Explore cell definition cell structure types of cells cell theory cell discovery and cell functions BYJUS. Pattern formation in the vascular system of monocot and dicot plant species. A typical seed includes three basic parts.
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Zygote divides by mitosis to form a proembryo. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce fermented bean paste nattō and tempehFat-free defatted soybean meal is a.
Criteria for classification of plants. The nodes hold one or more. Stomata regulate the process of transpiration and gaseous exchange.
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering.

Dicot Seed Diagram Quizlet

Cbse Class 10 Science Lab Manual Dicot Seed A Plus Topper Science Lab Seeds Science

Describe The Structure Of A Dicot Seed

Draw A Neat Diagram A Dicot Seed And Label Radicle On It

With The Help Of A Suitable Labelled Diagram Describe The Structure Of A Dicot Seed
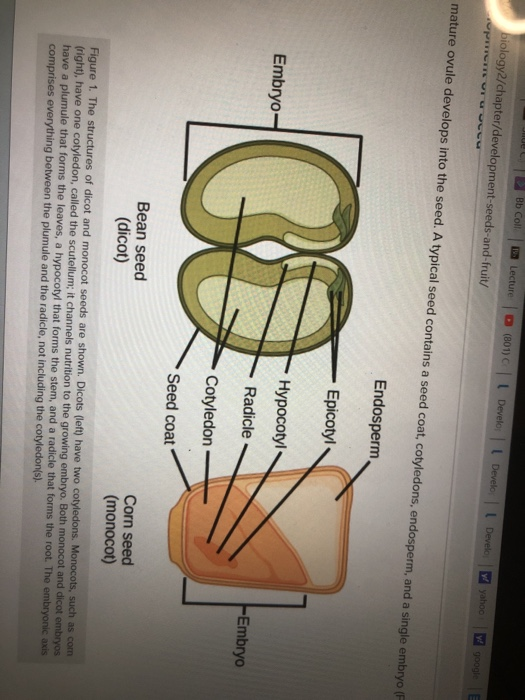
Solved 22 Read The Page On Monocot And Dicot Seeds See Chegg Com
Describe The Structure Of A Dicot Seed Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Bean Seed Structure Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock

Bean Seed Structure Dicot Stock Illustration Download Image Now Seed Bean Magnoliopsida Istock
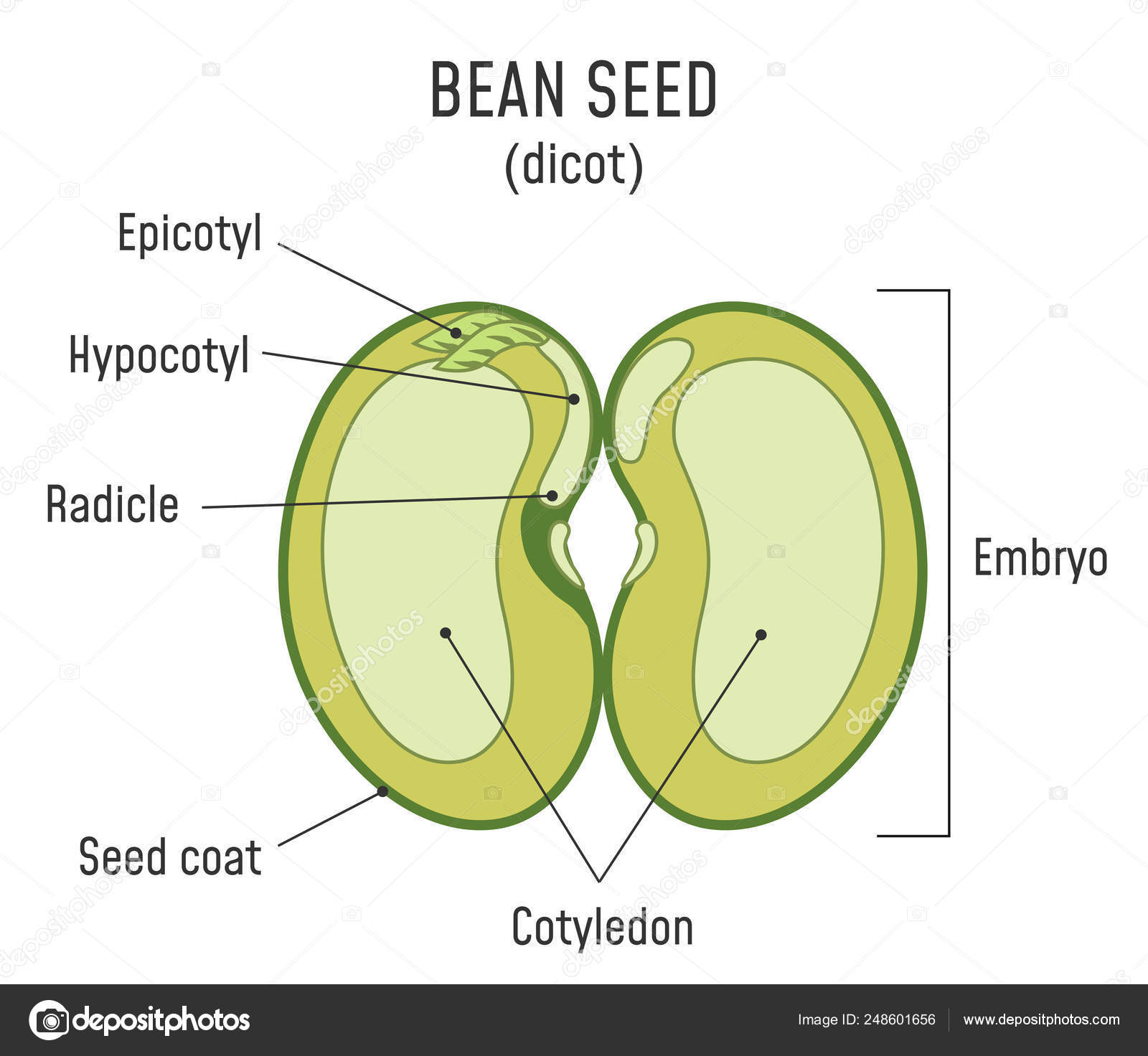
Bean Seed Structure Dicot Stock Vector Image By C Fancy Tapis Gmail Com 248601656
![]()
E5a2 Monocot Dicot Seeds On Vimeo
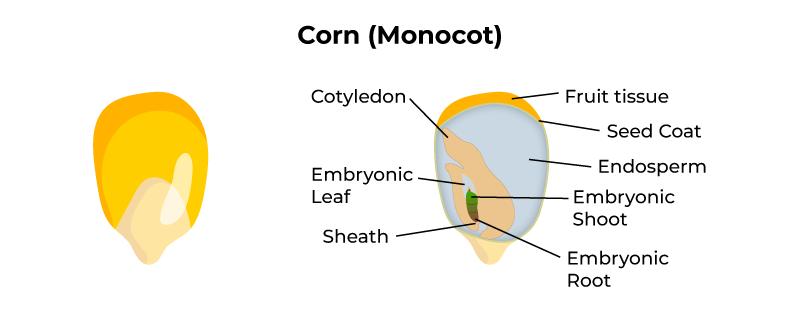
Structure Of Monocotyledonous Seed Geeksforgeeks
Anatomy Bean Seed Stock Illustrations 75 Anatomy Bean Seed Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
What Are Dicots Quora
Label The Dicot Seed Worksheet Enchantedlearning Com

Monocot Vs Dicot Seed Definition Structure 10 Differences Examples

Structure Of A Dicot And Monocot Seeds In Plants